출처 : https://linuxhint.com/change_mysql_data_directory_ubuntu/
How to Change MySQL/MariaDB Data Directory on Ubuntu – Linux Hint
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of
linuxhint.com
Now, change the owner and group of the /db directory to mysql with the following command:
$ sudo chown mysql:mysql /db

Now, you have to stop MySQL/MariaDB database service and copy all the files from the default data directory /var/lib/mysql to the new data directory /db.
If you’re using MariaDB, then stop MariaDB service with the following command:
$ sudo systemctl stop mariadb

If you’re using MySQL, then stop MySQL service with the following command:
$ sudo systemctl stop mysql

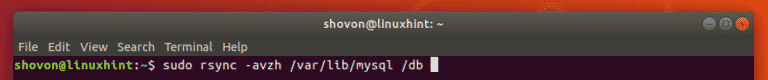
Now, copy all the contents of the default data directory /var/lib/mysql to the new data directory /db with the following command:
$ sudo rsync -avzh /var/lib/mysql/ /db
All the contents of /var/lib/mysql directory should be copied to the new directory /db.
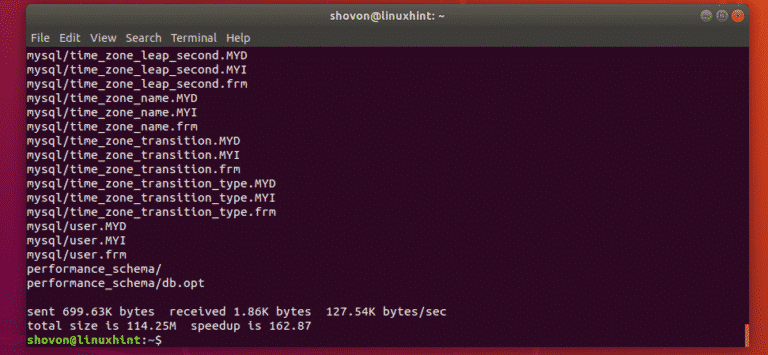
/db directory is now prepared to be the new MySQL/MariaDB data directory.
Configuring AppArmor:
Now, you have to configure AppArmor to allow /db to be a MySQL/MariaDB data directory.
To do that, edit the AppArmor alias file /etc/apparmor.d/tunables/alias as follows:
$ sudo nano /etc/apparmor.d/tunables/alias

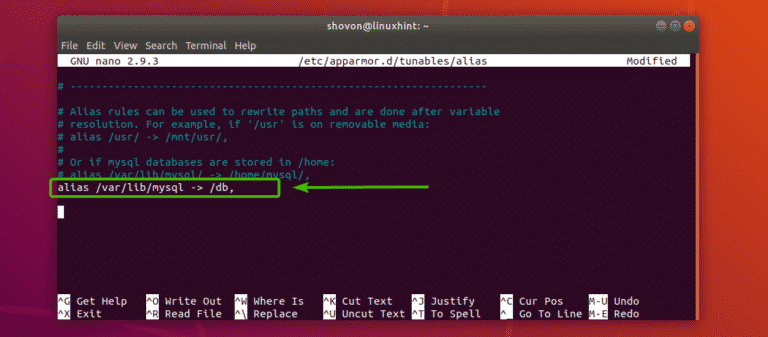
Now, add the following line at the end of the file and save it by pressing <Ctrl> + x followed by y and <Enter>.
alias /var/lib/mysql -> /db,
Now, restart apparmor service with the following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart apparmor
Now, you’re ready to change the data directory of MySQL/MariaDB.
Changing MySQL/MariaDB Data Directory:
To change the data directory from /var/lib/mysql to /db, you have to edit the required configuration file depending on whether you’re using MySQL/MariaDB.
If you’re using MariaDB, then the configuration file you have to edit is /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf.
If you’re using MySQL, then the configuration file to edit is /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf.
Now, edit the required configuration file depending on whether you’re using MySQL/MariaDB as follows:
MariaDB:
$ sudo nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
MySQL:
$ sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf

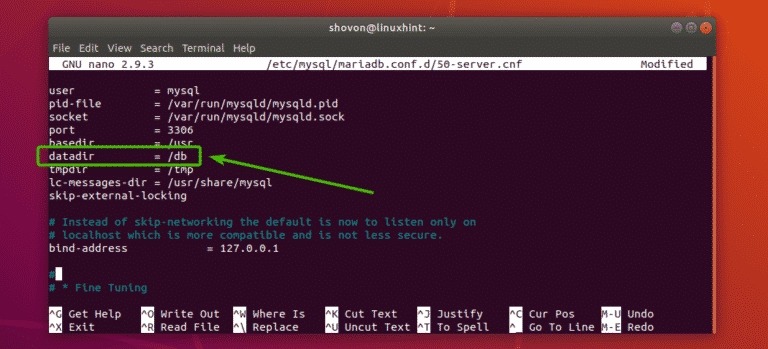
Now, find the line as marked in the screenshot below.

Change the datadir to /db as shown in the screenshot below. Then save the file by pressing <Ctrl> + x followed by y and <Enter>.
Now, start the MySQL/MariaBD service with the following command:
MariaDB:
$ sudo systemctl start mariadb

MySQL:
$ sudo systemctl start mysql

Testing MySQL/MariaDB:
Now, try to connect to the MySQL/MariaDB server as follows:
$ sudo mysql -u root -p

Then, type in the password of the MySQL/MariaDB server and press <Enter>.
You should be logged in to the MySQL/MariaDB shell as root database user. It’s an indication that it works.
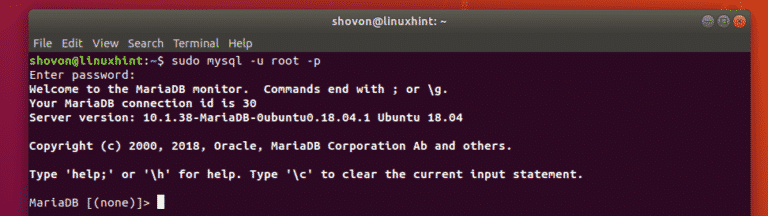
But, just to be sure, type in the following query to find which directory MySQL/MariaDB is currently using as the data directory.
sql> select @@datadir;
As you can see, the current data directory is /db just as I configured.

So, that’s how you change the MySQL/MariaDB data directory on Ubuntu. Thanks for reading this article.
'IT' 카테고리의 다른 글
| wordpress 테마 관련 wp-config.php 편집 (0) | 2021.08.05 |
|---|---|
| MariaDB 디렉토리 이동 완료 (1) | 2021.08.04 |
| DB 백업 스크립트 (0) | 2021.08.02 |
| RSS 생성 (0) | 2021.07.31 |
| 티스토리 추출 (0) | 2021.07.30 |
